
BoPing Wang, M.D.,PH.D
E-mail Address: wangboping2006@whu.edu.cn
Office Address: 185# DongHu Road, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071
Position(s): Lecturer
Affiliation(s):Department of Forensic Medicine
Research interests / Specialties:
Forensic Clinic, Forensic Genetics and Fish Chromosome Evolution
Education and Training
Medical Degree., 1993-1998 Hubei Medical College, China
M.S., 2001-2004 Medical College, Wuhan University, China
Ph.D., 2005-2013 College of Life Science, Wuhan University, China
Research Description
My research involves three fields: Forensic Clinic, Forensic Genetics and Fish Chromosome Evolution.
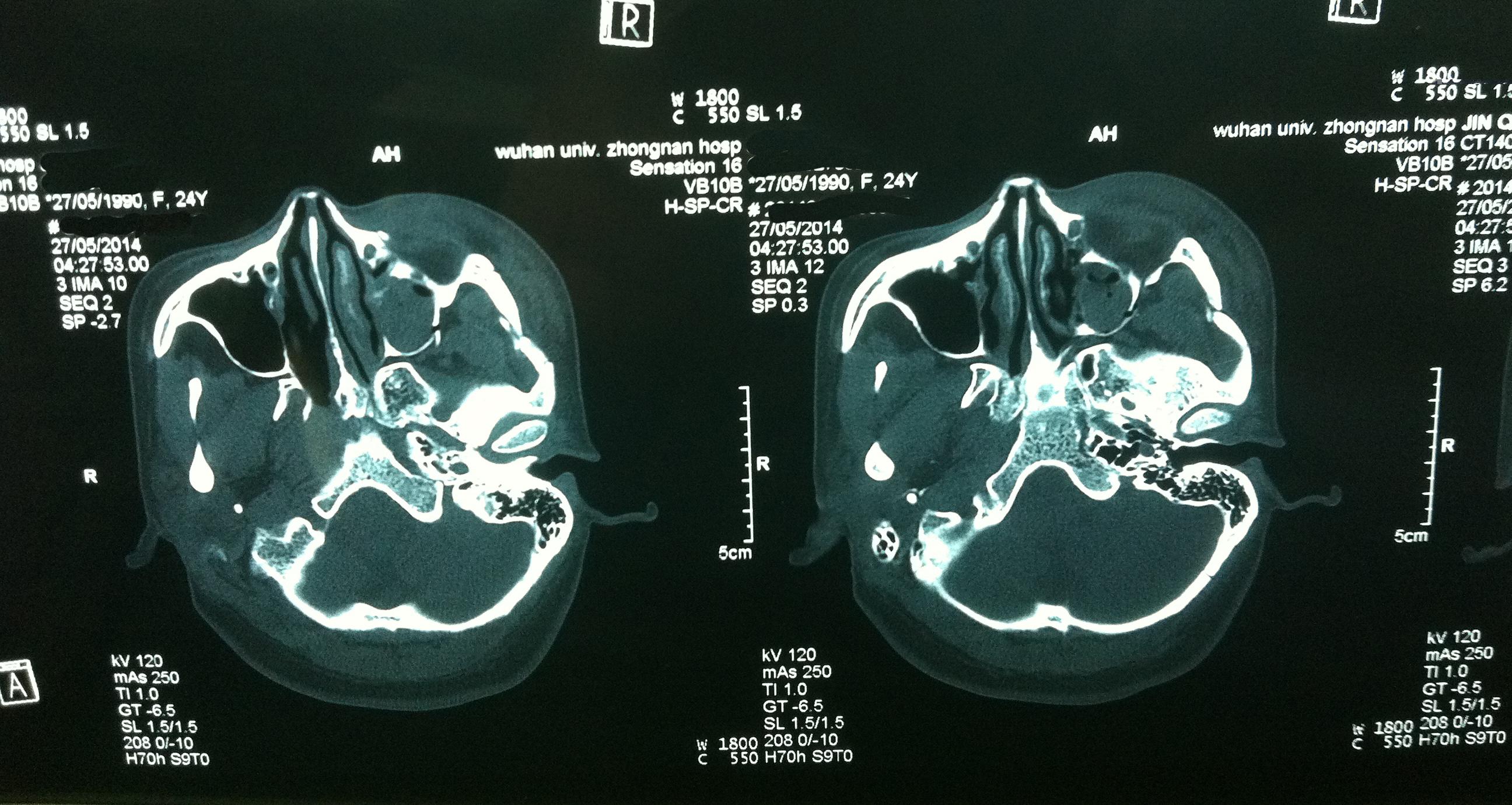
1. Forensic Clinic
I dealt with more than 5,000 cases in injuries, traffic accidents, medical tangles, etc. Sometimes I was invited to deal with troublesome cases.
My research focuses on how to distinguish injuries and diseases in troublesome cases, the relationships between injuries and diseases, the accurate time of injuries, etc.
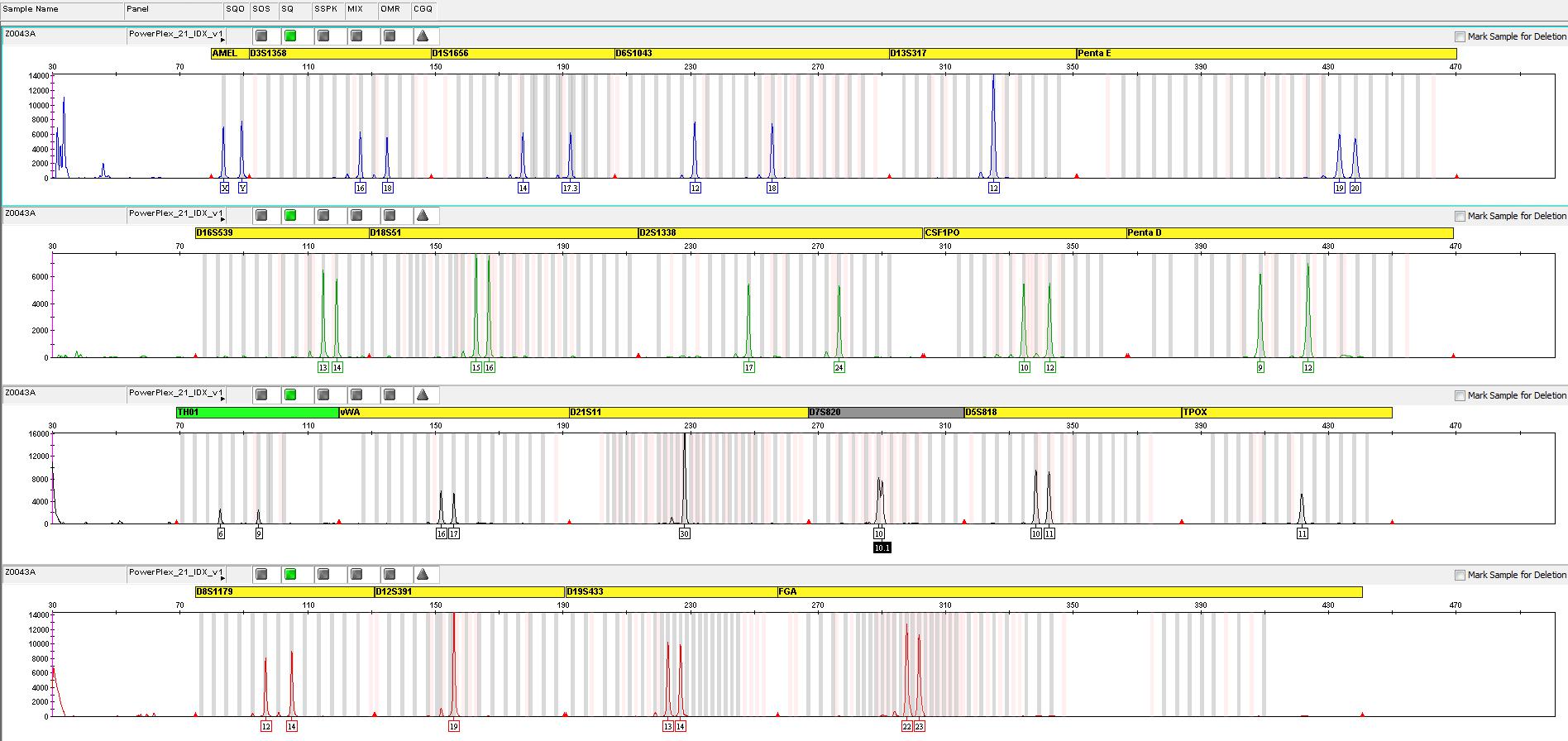
2. Forensic Genetics
I deal with lots of cases in paternity identification and personal identification. In 2014, I helped our department gained the score “consent” in the ability verification of paternity identification which was organized by Chinese government.
My research concerns the genotyping low copies of DNA template, and investigating the value of different biomarkers in forensic medicine.

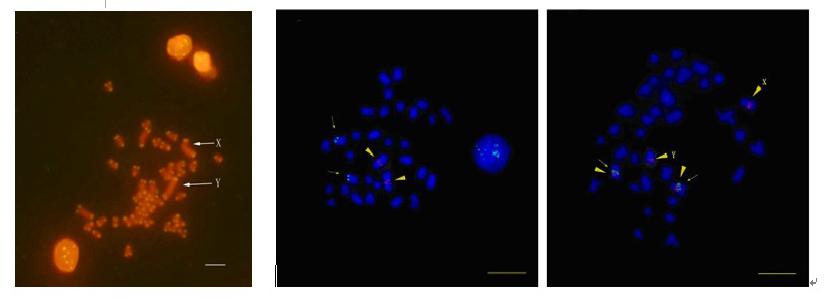
3. Fish Chromosome Evolution
During the period of PhD candidate, my research field was fish chromosome evolution, I am very interested in that field.
There are lots of repetitive DNA sequences (also named “jungle DNA”) in human or other animal genomes, such as Long Interspersed Repetitive Elements (LINE), Short Interspersed Repetitive Elements (SINE), Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (VNTR), etc. Up to now, little is known about their functions. However, those “jungle DNA” influence on chromosome evolution, even on species evolution.
I studied the fish chromosome evolution by using cytogenetic methods. The methods involved comparing the location of repetitive DNA sequences on different species chromosomes or sex chromosomes, sometimes concerned DNA sequencing, etc.
Publication list
1. Wang, B. P., Chen, J., Liu, J. D., Liu, N. & Yu, Q. X. (2011). Discriminating two races of Liobagrus marginatoides by cytogenetic analysis. Journal of Fish Biology.78, 2080-2084. (Published in English)
2. Gang Zhao, Qixing Yu, Ji Chen, Boping Wang, Yating Zang, Jiangdong
Liu.(2009). Repetitive DNA Sequences from the X Chromosome of the Spiny Eel (Mastacembelus aculeatus). Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences. 14, 183-188. (Published in English)
3. Rong Bao, Ping Yan, Rulin Li, Boping Wang, Chun Wang, Yuan he. (2006). An Analysis of 1219 Road Traffic Accident Injury Cases. Journal of Mathematical Medicine.19, 281-284. (Published in Chinese)
4. Boping Wang, et al. (2004).Genetic Polymorphism of DYS446 Locus in the
Wuhan Han Population. Journal of Mathematical Medicine.17, 109-110. (Published in Chinese)
5. Boping Wang, Hanhua Yu, Cunju Fu. (2003). Forensic Analysis of 114 Rib Fracture in Traffic Accident. Journal of Mathematical Medicine.16, 244-245. (Published in Chinese)


